Jumpstarting Tomorrow, a hybrid pilot grant/community-building program, supports innovative and collaborative teams that could become the vanguard for future strategic research investments by the university. The initiative was made possible through $2 million in funding to RDO from the first round of disbursements related to the UI utility public-private partnership (P3).
See below for information on the Round 1 awarded teams as well as how to connect with those team’s efforts.
Addressing Health Disparities and Biases in AI and Machine Learning Tools

Health disparities are defined by NIH as differences in the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and burden of diseases or health conditions between specific population groups in the US. These disparities are often associated with demographic, social or economic factors such as income, race, gender, and geography (e.g. rural vs. urban), among others. Iowa is not exempted from these disparities. Several recent studies have reported that AI systems can discriminate and create unequal outcomes in different population groups. Because AI/ML models learn from historically collected data, human and structural biases present in the data can be perpetuated and even exacerbated as the models are applied to clinical care. The goal of this initiative is to identify and quantify current biases in AI/ML healthcare models and to develop interventions to correct and reduce these biases.
Decarb 2040 – Positioning Iowa as an energy exporter in the coming era of deep decarbonization

Iowa’s abundant wind, bioenergy and solar resources make it a strong player in the emerging green energy landscape. By 2040, Iowa can become a net exporter of energy. Achieving net export status will bring energy independence to Iowa and will attract industries supplying and demanding clean energy. However, to achieve its potential Iowa needs to accelerate research, development, and adoption of low carbon energy production and storage methods. These technical elements must be coordinated with workforce development, innovation ecosystem, and public policy. Combining engineering, data science, public policy, environmental science, and business expertise, we will develop large proposals around the central question: how can R&D, education and outreach, markets, & socio-economic policy shift evolving barriers & attitudes towards adoption of carbon management practices & energy technologies?
Iowa Initiative for Scientific Imaging and Conservation of Cultural Artifacts (IISICCA)

This project brings together faculty and staff researchers from across the campus to develop non-destructive digital imaging, machine learning, and AI technologies to study cultural artifacts. AI will be used to study objects from the Iowa collections and to create a database of materials, texts, and other object properties from known samples. The approach combines volumetric X-ray and multispectral optical imaging trained on a control dataset of materials of known composition to determine unknown material properties, design, structure, and repair status of 3D artifacts, and the ink/pigment components of pre-modern texts. We employ the novel use of 21st-century technology to establish early standards for future imaging research and to reveal data about cultural artifacts and their previously undiscoverable secrets. Aim-4 will study 13th–20th century African artifacts, 12th–15th century manuscripts, and 16th century rare books.
Jumpstarting a Quantum Simulation Program at The University of Iowa
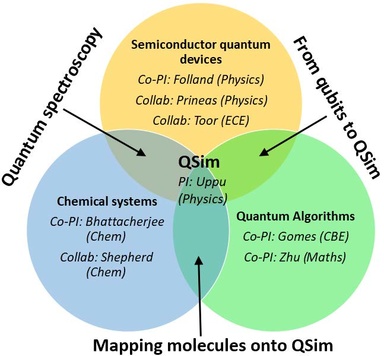
Quantum simulation (QSim) can enable efficient discovery of drugs, biocompatible fertilizers, and high temperature superconductors, all key priorities as identified by the United Nations. Such simulations are not possible even with the largest supercomputers due to the limits of conventional computation, but quantum computers would be capable of solving these problems. This proposal aims to solve the convergent problem of constructing a practical QSim leveraging unique expertise at UI by creating a team of physicists, chemists, engineers, and mathematicians to concurrently tackle the fundamental as well as technical challenges. We aim to implement a practical and scalable QSim by i) developing semiconductor qubits operating at higher temperatures and lower costs than associated with competing technology and ii) building on UI strengths in nanofabrication (Iowa CREATES) and quantum algorithms. The long-term goal (<5 years) of placing UI on the map as a leader in quantum science research and development.
Public Libraries for Disaster Resilience: Assessing Libraries’ Community Impacts in Times of Climate and Socio-Economic Crises

How do public libraries mitigate community vulnerabilities and build resilience to climate, social, and economic risks? Libraries provide welcoming spaces and essential services during crises: shelter from extreme heat/cold waves for the poor and homeless, internet access, job search and training during economic recessions, and reliable information during crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Using spatial, quantitative, qualitative, and social media data mining methods, the project will yield a public-facing report of the findings, produce scholarly publications, and serve as a pilot study for several major external grant proposals. This project will also utilize team-building methods to develop a launching platform for a sustainable UI interdisciplinary research group focused on Community Resilience. The Core Team includes scholars from the School of Library and Information Science, the School of Planning and Public Affairs, the Department of Sociology and Criminology, and the Tippie College of Business.
